Description
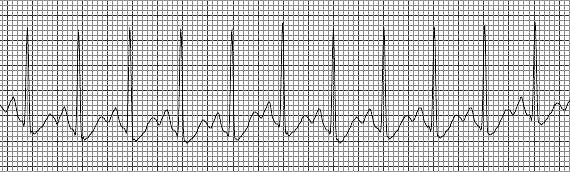
Sinus tachycardia (often referred to as sinus tach) is a rhythm which is formed by the electrical impulse originating in the SA node in the normal manner. However, the rate is faster than normal. The normal heart rate range is 50-100 beats per minute in adults. The rate in the example above is 150 beats per minute. It is also not unusual for both the PR and QT intervals to decrease in length with increased rates.
This is a common rhythm which in response to any of a variety of stimuli is completely normal. The following are situations in which sinus tachycardia is normal;
- Response to exercise (even running up a flight of stairs)
- Emotional upset or anxiety
- When running a fever
- When a patient is pregnant
- When ingesting caffeine or alcohol
- Smoking
There are also situations when the rhythm is in response to an abnormal physiologic condition such as the following;
- Hypotension/hypertension
- Congestive heart failure
- Shock
- In the presence of heart disease
- During a heart attack
A patient’s normal maximum heart rate decreases with age. At age 16, maximum rates under exertion of 220 beats per minute would not be unusual. However, by age 50, that same persons maximum rate under exertion may decrease to 160 beats per minute.
Patients experiencing sinus tachycardia may complain of rapid rates, palpitations, dizziness, lightheadedness or any of a variety of related symptoms. Generally, no treatment is necessary in the presence of sinus tachycardia. However, if the sinus tachycardia is an inappropriate response (for example, patient is sitting still and is in sinus tachycardia), medications may be indicated.